Understanding information registers
The Information register configuration object is intended to describe a multidimensional data storage structure. The platform uses the Information register configuration object as the basis for creation of database tables that store custom multidimensional data (fig. 9.1).
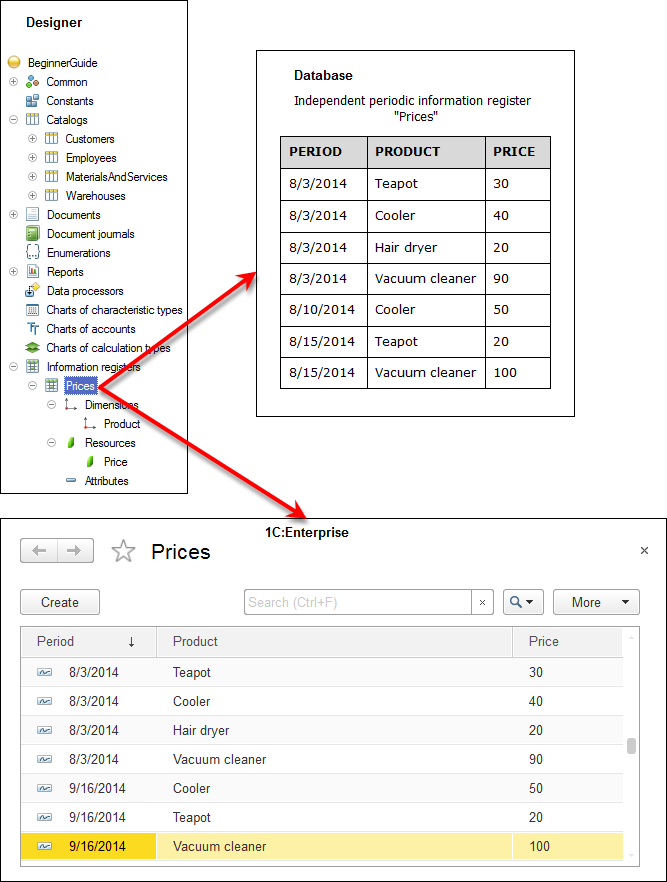
Fig. 9.1. The Prices independent periodic information register in Designer and in the database
The main difference between an information register and an accumulation register is the fact that each information register record sets a new resource value, while each accumulation register record modifies the current resource value. Because of this difference, an information register can store data of any type (rather than just numeric, as was the case with an accumulation register).
Another important characteristic of an information register is its ability to store data with time stamps if required. So it can store not only the current data values but also their changes with time. If an information register uses time stamps, it is referred to as a periodic information register.
The information register periodicity can have one of the following values:
- Within a second
- Within a day
- Within a month
- Within a quarter
- Within a year
- By recorder position (if the write mode is set to Subordinate to recorder)
Periodic information registers always contain the system Period field, which is added automatically. It has the Date type and specifies the period where a record belongs. When writing data to a register, the platform changes the value of the Period field to the beginning of the register period that includes that value.
For example, if data is written to an information register with periodicity "within a month" and the period for that data is set to 4/8/2014, the register stores the data with the period value 4/1/2014.
As with other registers, the platform ensures the uniqueness of information register records. However, while other registers use the recorder and row number as unique identifiers, information registers use a different key value generation method.
An information register record key, which uniquely identifies a record, consists of all register dimensions and a period (in case of a periodic information register). For example, the key of the periodic information register that has the Product dimension and the Price resource (see fig. 9.1) is a set of Period and Product field values. An information register cannot contain multiple records with identical keys.
Compared to an accumulation register, an information register offers greater freedom in editing the data it contains. In addition to information registers that are subordinate to recorders (their records are "bound" to the recording documents), information registers that can be freely edited by users are available. An information register that is not subordinate to a recorder is referred to as independent information register.
Learn more! For details on the structure of 1C:Enterprise script objects intended for information register operations, see section Quick developer reference. Information registers.
