1C:Enterprise 8.3. Administrator Guide. Contents
1C:ENTERPRISE INSTALLATION
1C:Enterprise is a collection of software modules designed to develop and use solutions (configurations) for accounting and enterprise business activities automation, as well as configurations or collections of configurations.
1C:Enterprise software modules are universal and can work with any configuration (within the scope of the corresponding License Agreement).
The security driver to prevent unauthorized access is installed with 1C:Enterprise.
The installer makes it possible to install multiple 1C:Enterprise versions on a single computer, select the components to install and choose a version of 1C:Enterprise server installation.
The launcher that is part of 1C:Enterprise makes it possible to work with a single list of infobases created in all versions of 1C:Enterprise (versions 8.0, 8.1, 8.2 and 8.3).
2.1. GENERAL INFORMATION ON INSTALLATION PROCEDURE
There are significant differences between installation procedures of 1C:Enterprise under Microsoft Windows operating systems (hereinafter Windows) and under Linux operating systems (hereinafter Linux).
For Windows a dedicated installer is used (see page 24).
No such installer is available for Linux so specific instructions on actions to be taken to carry out an operation will be provided in the respective sections (see page 36).
Before installation, please ensure that your computer is virus-free and that the hard drive does not contain any errors and enough disk space is available for the installation.
NOTE
In the installation process you may need the distribution packages of the operating system running on the computer. You may also need to possess the local or network administrator rights.
2.2. WINDOWS INSTALLER
2.2.1. Available Installers
The following installers are available:
1C:Enterprise 8 – allows to install any component except 64-bit 1C:Enterprise server version.
1C:Enterprise 8 Thin Client – for installation of only the components that are required to access 1C:Enterprise server and of the thin client itself.
1C:Enterprise 8 (x86-64) – installs 64-bit 1C:Enterprise server version.
All the installers share the same operation principles so we will provide the general information on 1C:Enterprise 8.3 installer.
2.2.2. General Information on Installer
A dedicated wizard carries out the installation procedure. You can navigate through the wizard pages with the Next >> button. To launch the wizard, run setup.exe from the directory of the distribution kit you have selected. On every page you will be prompted to provide some information that will be further used for 1C:Enterprise installation.
This software will be installed in the following cases:
When the user launching the installer is a member of the local administrators group.
When the user launching the installer is not a member of the local administrators group but software installation is permitted for the user and the computer concerned (AlwaysInstallElevated register key).
Every wizard step is briefly described below.
NOTE
If you run setup.exe using /S option, the software will be installed in "silent" mode based on the settings stored in the 1CEStart.cfg file (see page 241) while if the file is not available, default installation will be carried out.
When you run the installer you can specify the USEHWLICENSES parameter, which controls the search of the the protection key when 1C:Enterprise is launched. For example, the command line listed below sets writes the parameter UseHwLicenses=0 to the 1CEStart.cfg file (see page 241) for the user, which performes the installation of 1C:Enteprise:
setup.exe USEHWLICENSES=0
NOTE
You can specify the USEHWLICENSES parameter in the setup.ini file, in the CmdLine option of the Startup group.
2.2.2.1. Welcome!
This is the initial window of the 1C:Enterprise installation wizard.
Fig. 1. Welcome!
2.2.2.2. Components Selection
On this page you will need to select the components to install and the installation folder. The selection of the components depends on what you need to install. Some standard installation scenarios are described below (see page 32).
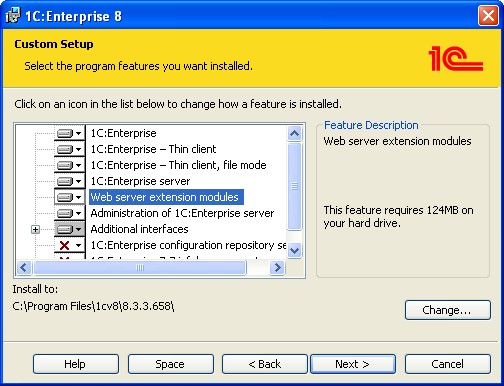
Fig. 2. Components Selection
If a certain component needs to be installed, check it. If some component is not needed, deny its installation. To select a component, click an icon to the left of the component name (or press the Spacebar). In the menu that opens you should select the appropriate item (see fig. 3).
Fig. 3. Component Installation Menu
The components to be installed and the denied components are displayed in the manner shown in fig. 4.

Fig. 4. Allowed and Denied Components
Here is a brief explanation of the components being installed:
|
Component |
Brief Description |
|
1C:Enterprise |
Basic 1C:Enterprise components, including components for administration, configuration development, thick and thin clients. |
|
1C:Enterprise – Thin client |
Only the components of the thin client intended to work in the client-server mode. |
|
1C:Enterprise – Thin client, file mode |
Thin client components, including those intended to work with the file infobase. |
|
1C:Enterprise server |
1C:Enterprise server components, including administration server and administration utility. |
|
Web server extension modules |
Web servers extension modules that are required for web client and web services operation. |
|
Administration of 1C:Enterprise server |
Additional components that are required to administer the 1C:Enterprise server cluster. |
|
Additional interfaces |
User interfaces in various languages. |
|
1C:Enterprise configuration repository server |
1C:Enterprise configuration repository server components. |
|
1C:Enterprise 7.7 infobase converter |
Converter of infobases created in 1C:Enterprise 7.7 (outdated version). |
Regardless of where 1C:Enterprise is installed (the Install to: field and the Change button), some folders of the installed system will be placed in fixed locations. For details, see page 223.
After successful installation, a local configuration file will be created (see page 241 for details) for all the users where two parameters will be installed: Instal- ledLocation and InstallComponents. The values of these parameters will be installed in accordance with the settings established during system installation.
2.2.2.3. Selecting Default Interface Language
At the next step the installer will prompt you to select a default interface language.

Fig. 5. Selecting Interface Language
You should specify one of the available interface languages as the default one.
When the installer completes the installation, the conf.cfg file (see page 245) will be created in the C:\Program Files\1Cv8\conf directory to describe the default interface language.
If in your work you need to use an interface language other than the one installed as the default language, you should specify this language using the /L command line option:
|
Interface Language |
Language Code |
|
Azerbaijani |
az |
|
English |
en |
|
Bulgarian |
bg |
|
Georgian |
kk |
|
Interface Language |
Language Code |
|
Kazakh |
ka |
|
Chinese |
zh |
|
Latvian |
lv |
|
Lithuanian |
lt |
|
German |
de |
|
Polish |
pl |
|
Romanian |
ro |
|
Russian |
ru |
|
Turkish |
tr |
|
Ukrainian |
uk |
|
Vietnamese |
vi |
2.2.2.4. 1C:Enterprise Server Installation
If 1C:Enterprise server component is selected to be installed, the wizard page will be available where one should select the installation mode for the 1C:Enterprise server and the user account the server will run under, if it is installed as a Windows service.
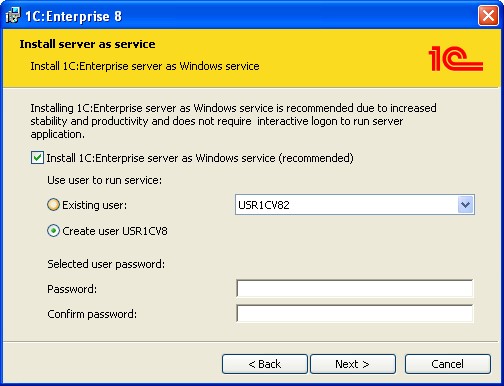
Fig. 6. 1C:Enterprise Server Installation Mode
NOTE
If one chooses to install the server as a service, you will need to specify the password for the user selected because otherwise the installer will be unable to launch the server.
If some 1C:Enterprise version is already installed on the computer with its server installed as a Windows service, the installer will reinstall the service.
2.2.2.5. Installation Initialization
Pressing the Install button begins the actual installation process:
The required folders are created
The files for the selected components are copied
Configuration files are created
Software components are registered
A desktop shortcut is created to launch 1C:Enterprise
1C:Enterprise server is launched if installation as a Windows service was selected for the server
Fig. 7. Installation Initialization
At that one can see an individual installation record for every installed version in the Add/Remove Programs of the Windows control panel, displayed as follows: 1C:Enterprise 8.3 (8.3.3.657).
2.2.2.6. Security Driver Installation
When installation is completed, the installation wizard prompts to install the HASP Device Driver security driver for protection from unauthorized use.
Fig. 8. Security Driver Installation
The driver needs to be installed if a dongle will be plugged into a USB port of this computer:
The user has a License Agreement for 1C:Enterprise operation on a single workstation;
The user has a Supplemental License Agreement for 1C:Enterprise operation on a single additional workstation;
The user has a License Agreement for 1C:Enterprise server use.
NOTE
We recommend installing security driver prior to plugging the dongle into the USB port of the computer.
The driver can also be installed using the Start – Programs – 1C Enterprise 8.3 – Advanced – Install HASP Device Driver.
2.2.2.7. Completion of the Installation
If software installation is successful, the final page of the installation wizard will be opened. Once you click the Finish button, the installation will be completed.
If Show the readme file is checked, a file will be opened that contains the information that we recommend reading prior to using this software version.
Fig. 9. Installation Complete
2.3. STANDARD 1C:ENTERPRISE INSTALLATION SCENARIOS
This section provides tips on carrying out standard versions of 1C:Enterprise installation.
2.3.1. Windows
This section covers standard examples of 1C:Enterprise components installation on a computer running a Windows operating system.
For every installation version we will provide a list of the installed components and the specific issues that should be taken into account in the installation process (if any).
2.3.1.1. Thin and Thick Clients
To proceed with this 1C:Enterprise installation option, you will need to allow the following components to be installed:
1C:Enterprise
1C:Enterprise – Thin client, file mode
If a local dongle is used, one should also install the HASP Device Driver security driver (see page 183). The driver should be installed prior to inserting the dongle into the computer USB port. If a network software protection key is used, it is not necessary to install the HASP Device Driver protection driver. For details on setting up dongle access, see page 181.
One can launch:
Designer
Thin client
Thick client
The following infobases can be used:
File infobase, local mode
File infobase, network mode
Client/server mode
Any infobase accessed via a web server
2.3.1.2. Thin Client
To install 1C:Enterprise thin client, installation of 1C:Enterprise – Thin client, file mode should be allowed.
If a local dongle is used, it is required to install the HASP Device Driver protection key driver (see page 183). Install the driver before the dongle is inserted into a USB plug of the computer. If a network dongle is used, there is no need to install the HASP Device Driver protection key driver. For more information on customizing access to the dongle, see page 181.
Only thin client can be launched.
The following infobases can be used:
File infobase, local mode
File infobase, network mode
Client/server mode
Any infobase accessed via a web server
NOTE
If this installation option is used, it will be impossible to develop configurations.
2.3.1.3. Thin Client – Client/Server Operation Mode
To install this option of 1C:Enterprise, installation of 1C:Enterprise – Thin client should be allowed.
If a local dongle is used, it is required to install the HASP Device Driver protection key driver (see page 183). Install the driver before the dongle is inserted into a USB plug of the computer. If a network software protection key is used, there is no need to install the HASP Device Driver protection key driver. For more information on customizing access to the dongle, see page 181.
The thin client may be launched.
The following infobases can be used:
Client/server operation mode
Any infobase accessed via a web server
NOTE
If this installation variant is used, it will be impossible to develop configurations.
2.3.1.4. Thick Client
To install 1C:Enterprise thick client, one needs to allow installation of 1C:Enterprise.
If a local dongle is used, you should also install the HASP Device Driver security driver (see page 183). The driver should be installed prior to plugging the dongle into the computer USB port. If a network software protection key is used, there is no need to install the HASP Device Driver protection driver. For details on setting up dongle access, see page 181. The following software can be launched:
Designer
Thick client
The following infobases can be used:
File infobase, local mode File infobase, network mode
Client/server operation mode.
2.3.1.5. Configuration Repository Server (TCP)
In order to install the 1C:Enterprise Configuration Repository server to work via TCP (see "1C:Enterprise 8.3. Developer Guide"), one has to allow installation of 1C:Enterprise configuration repository server.
NOTE
The Configuration Repository server is a 32-bit application.
2.3.1.6. Configuration Repository Server (HTTP)
In order to have the 1C:Enterprise Configuration Repository server installed on a computer to work via HTTP (see "1C:Enterprise 8.3. Developer Guide"), you need to allow installation of the following components:
Web server extension modules
1C:Enterprise configuration repository server
NOTE
The Configuration Repository server is a 32-bit application.
2.3.1.7. Enabling Web Client or Web Service Publication
In order to be able to publish a web client on the computer where the software is installed, please add the Web server extension modules component to the selected components (if it is not yet selected).
To publish a web client or a web service, use the publication dialog on the web server or the webinst utility (only the web client). For a detailed description of these tools, please see page 147.
2.3.1.8. Enabling Designer Use
In order to be able to use the Designer, you should add 1C:Enterprise component to the set of the components required for a specific installation (unless it is already selected).
2.3.1.9. Installation Using Windows Administration Tools
Group Policies-Based Installation
When Group Policies are used in the installation process, in order to select the installation language you will need to specify the corresponding transformation language file. File names follow LCID Microsoft Windows decimal format (with .mst extension). The transformation file for the Russian language is named 1049.mst.
Besides, the adminstallrestart.mst transformation file should be specified. In this case, if client and server versions do not match, 1C:Enterprise will prompt to restart the computer to install a new version. Administrator must ensure that the new distribution kit has already been added in the Group Policies. Multiple 1C:Enterprise versions can be installed using Group Policies.
To install a new version, a new installation instance in the Group Policies should be created.
Logon Script-Based Installation
A script executed when a user logs on to a domain can be used for installation. The corresponding script is specified by the domain administrator.
If a user does not possess enough rights to install software, the administrator will need to specify that installation script will be executed under the user account with sufficient rights. For an example of the script, see page 247.
Multiple 1C:Enterprise versions can be installed and uninstalled using such a script. To do so, you need to call the installOrUninstall procedure with the required parameters (for an example of the script, see page 247).
To install a new version, the administrator will simply need to edit the paths of network shares and the product code that should be taken from the setup.ini file.
Besides, the adminstallrelogon.mst transformation file will need to be specified. In this case when client and server versions do not match, 1C:Enterprise will prompt to shut the current user session down to install a new version. Administrator will need to ensure that the script is up-to-date and the distribution kit for the new version is available in the network resource. Version Update
If the platform is installed using the administration tools, adminstall.cfg (see page 247) is created in the configuration files directory (see page 227).
If the required 1C:Enterprise version cannot be found on the computer when an infobase is launched, or if the current user does not possess enough rights to install the required version, the user will be prompted to carry out the action specified in adminstall.cfg: restart the computer or retry the logon.
2.3.2. Linux
This section covers standard examples of 1C:Enterprise Configuration Repository server installation on a computer running a Linux operating system.
The following information is provided for installation packages for the 32-bit RPM version. The installation is performed by the package manager of the OS used.
The 1C:Enterprise distribution set for Linux is comprised of a number of packages. They are used to install both client applications and the server:
1c_enterprise83-client-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-client-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-common-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-common-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-crs-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm (only for the i386 architecture)
1c_enterprise83-server-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-server-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-thin-client-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-thin-client-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-ws-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-ws-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
When a client application is installed, start the /opt/1C/v8.3/i386/utils/config_system utility (or /opt/1C/v8.3/x86_64/config_system for the 64-bit version), which will: check the availability of all the libraries required for proper server functioning;
register the installed TrueType fonts in ImageMagick. If the fonts installed cannot be found, the script will ask you to specify the directory where the files are located.
CAUTION
The config_system utility should be run by the system administrator.
Packages include the following components:
1c_enterprise83-client – 1C:Enterprise client applications (thick client and thin client);
1c_enterprise83-thin-client – 1C:Enterprise thin client (working with the infobase in file mode is not supported);
1c_enterprise83-common – 1C:Enterprise common components;
1c_enterprise83-server – 1C:Enterprise server components;
1c_enterprise83-ws – adapter for publishing 1C:Enterprise web services on a web server based on Apache HTTP Server 2.0 or Apache HTTP Server 2.2;
1c_enterprise83-crs – components of the 1C:Enterprise configuration repository server (the repository server is a 32-bit application).
Packages with the -nls suffix in their names are additional national resources (except for English and Russian) for a respective package. For example, the 1c_enterprise83-server-nls package includes additional national resources (except for English and Russian) for 1C:Enterprise server components.
NOTE 1
For 64-bit RPM versions of 1C:Enterprise for, the .x86_64 symbols should be specified instead of .i386 in file names. For instance, the name of the 1c_enterprise83-ws-8.3.1-100.i386.rpm file will change to
1c_enterprise83-ws-8.3.1-100.x86_64.rpm.
NOTE 2
For 64-bit 1C:Enterprise versions for Debian Linux, specify the _amd64 symbols instead of .i386 in file names. For instance, the name of the 1c-Enterprise83-ws_8.3.1-100_i386.deb file will change to 1c-Enterprise83-ws_8.3.1-100_amd64.deb.
NOTE 3
Installation files for DEB systems will have a name that differs from the name of the same files for RPM systems only by its extension: deb. For instance, the name of the 1c_enterprise83-ws-8.3.1-100.i386.rpm file will be 1C_Enterprise82-ws-8.30.1-100.i386.deb.
Consider the following dependencies during the installation:
1c_enterprise83-common has no dependencies;
1c_enterprise83-server depends on 1c_enterprise83-common;
1c_enterprise83-ws depends on 1c_enterprise83-common;
1c_enterprise83-crs depends on 1c_enterprise83-common, 1c_enterprise83server and 1c_enterprise83-ws;
1c_enterprise83-client depends on 1c_enterprise83-server;
1c_enterprise83-thin-client has no dependencies. The thin client does not require that other packages from 1C:Enterprise be installed. It conflicts with the 1c_enterprise83-common package. Either 1c_enterprise83-thin-client or the other packages can be installed;
National resource packages depend on their respective components.
Therefore, to install any package successfully, you should first install all the packages it depends on. For instance, to install 1C:Enterprise server components, you should install the 1c_enterprise83-common package first and then 1c_enterprise83server.
When client applications are installed, shortcuts to start the software (1cestart), the thin client (1cv8c) and the thick client (1cv8) are added to the desktop environment application menu. The shortcuts will be generated only for applications actually installed. Shortcuts belong to the Finance subcategory of the Office category.
The installation is executed by the root user.
2.3.2.1. Thin and thick clients
This 1C:Enterprise installation option requires the following packages to be installed:
1c_enterprise83-common-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-common-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-server-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-server-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-client-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-client-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
If a local client key is used, you need to install the HASP Device Driver (see page 189).
Install the driver before the dongle is inserted into a USB plug of the computer. There is no need to install the HASP Device Driver if a network software protection key is used. For more information on customizing access to the dongle, see page 181. You can run:
Designer
Thin client
Thick client
You can use the following infobases:
File infobase, local mode
File infobase, network mode
Client/server mode
Any infobase via a web server
2.3.2.2. Thin client
This 1C:Enterprise installation option requires the following packages to be installed:
1c_enterprise83-thin-client-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-thin-client-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
If a local client key is used, you need to install the HASP Device Driver (see page 189). Install the driver before the dongle is inserted into a USB plug of the computer. There is no need to install the HASP Device Driver if a network software protection key is used. For more information on customizing access to the dongle, see page 181.
You can run the thin client.
You can use the following infobases:
File infobase, local mode
File infobase, network mode
Client/server mode
Any infobase via a web server
NOTE
Configuration development is not available when this installation option is used.
2.3.2.3. Configuration Repository Server Installation (TCP)
In order to have the 1C:Enterprise Configuration Repository server installed on a computer to work via TCP (see "1C:Enterprise 8.3. Developer Guide"), you need to allow installation of the following components (of the specific version):
1c_enterprise83-common-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-common-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-server-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-server-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-crs-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
NOTE
The Configuration Repository server is a 32-bit application.
2.3.2.4. Configuration Repository Server (HTTP)
In order to have the 1C:Enterprise Configuration Repository server installed on a computer to work via HTTP (see "1C:Enterprise 8.3. Developer Guide"), you need to allow installation of the following components (of the specific version):
1c_enterprise83-common-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-common-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-Server-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-Server-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-ws-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-ws-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-crs-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
NOTE
The Configuration Repository server is a 32-bit application.
2.3.2.5. Web Client Operation
In order for you to be able to use the web client, the following packages should be installed on the web server computer:
1c_enterprise83-common-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-common-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-server-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-server-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-ws-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-ws-nls-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
1c_enterprise83-crs-8.3.<X>-<Y>.i386.rpm
The web client will be published with the webinst command-line utility (see page 155).
NOTE
The 1c_enterprise83-crs-8.3.<X>-<Y> package is only intended for the i386 architecture.
2.4. SYSTEM DEPLOYMENT RECOMMENDATIONS
In order to facilitate automatic installation of new 1C:Enterprise versions on user computers (including the initial installation), it is recommended to place the files in the network directory as follows:

Fig. 10. Directory structure
Where:
\\Server\1CEDistr – a directory on the Server server that contains the files required for deployment.
1cestart.exe – the launcher. To perform initial installation, run the launcher from this network directory. The software should be taken from the newest 1C:Enterprise 8.3 version planned for installation.
ibcommon.v8i – a list of common infobases if available (the name is conventional and optional). For descrition of the file format see page 235.
1CESCmn.cfg – a common configuration file. Specifying the following parameters is recommended:
○ CommonInfoBases=CommonInfoBasesListFileName. v8i – if it is necessary for the user to have the required infobase list at system startup. For a description of this parameter, see page 235.
○ InstallComponents – specify the components that need to be installed on user computers. For a description of this parameter, see page 240.
○ DistributiveLocation – specify the 1C:Enterprise distribution kit directory. For a description of this parameter, see page 240.
8.3.1.100 and 8.3.1.150 – the directories containing the distribution kits for the corresponding versions of 1C:Enterprise.
setup.exe – the file for launching 1C:Enterprise program installation.
The following shared configuration file is used in this example (all components and languages – Russian and English – are installed).
Content of the 1CESCmn.cfg file:
CommonInfoBases=ibcommon.v8i DistributiveLocation=\\Server\1CEDistr InstallComponents=DESIGNERALLCLIENTS=1 SERVER=1 WEBSERVEREXT=1 CONFREPOSSERVER=1 SERVERCLIENT=1 CONVERTER77=1 LANGUAGES=en
IMPORTANT!
The common 1CESCmn.cfg configuration file must not be located on the user’s computer!
When a new version of 1C:Enterprise is released (e.g., 8.3.1.200), you will only need to copy the distribution kit files to the \\Server\1CDistr\8.3.1.200 directory, and the system will perform the remaining required actions automatically when the user starts 1C:Enterprise.
When working with such a deployment scheme, please remember the following:
If 1C:Enterprise is installed using the launcher, it is always installed in the default directory. To change this directory, run the installer (setup.exe) of the appropriate version manually.
Only the InstallComponents parameter from the common configuration file is used during installation. Other parameters do not impact the installation process and are not transferred from the shared configuration file into the local one. The following components will be used in the example described above:
InstallComponents=DESIGNERALLCLIENTS=1 SERVER=1 WEBSERVEREXT=1 CONFREPOSSERVER=1 SERVERCLIENT=1 CONVERTER77=1 LANGUAGES=en
The CommonCfgLocation parameter is written into the local configuration file during installation. The value of this parameter is the path to the shared configuration file from the deployment directory. The path to this file in the example described above will appear as follows: \\server\1cdistr\1CESCmn.cfg. From that point, the parameters specified in this file will be used by the launcher and in the client application startup dialog (see page 94).
2.5. ADDITIONAL SOFTWARE INSTALLATION AND SETUP
2.5.1. Windows
2.5.1.1. OS authentication when using Apache web server
It is possible to configure support of OS authentication for the thin and the web clients when Apache web server is used. In this section, we assume that Apache web server is already installed and configured for access through a web client.
IMPORTANT!
In order to configure OS authentication, the network should have PDC deployed under Windows 2000 or later.
To perform setup:
Install mod_auth_sppi authentication module. The module is located at:
http://sourceforge.net/projects/mod-auth-sspi. The module version should match the used Apache version;
Copy mod_auth_sspi.so to the modules subdirectory of the Apache setup directory;
Add the following string to the httpd.conf configuration file of the Apache web server:
LoadModule sspi_auth_module modules/mod_auth_sspi.so
Add the following strings to the section describing the required virtual directory (the lines are highlighted in bold):
<Directory "c:/www/MyApp"> AllowOverride None Options None Order allow,deny Allow from all SetHandler 1c-application ManagedApplicationDescriptor c:/www/MyApp/default.vrd AuthName "1C:Enterprise web client" AuthType SSPI SSPIAuth On SSPIAuthoritative On SSPIPackage Negotiate SSPIOfferBasic Off Require valid-user </Directory>
Check Trust computer for delegation in the user account properties on the computer running the web server; Restart the web server.
2.5.2. Linux
2.5.2.1. Specific Settings for Working in the File-Mode Infobase
When working in the file-mode infobase on a computer running Linux, the following specific aspects must be taken into account:
When connecting to a network resource in Linux using the mount.cifs command, do not use the nobrl key (http://www.samba.org/samba/docs/man/manpages-3/ mount.cifs.8.html).
When providing access to the directory with an infobase using the Samba system, do not apply the locking=no parameter to the resource being published in the smb.conf file (http://www.samba.org/samba/docs/man/manpages-3/ smb.conf.5.html).
If multiple users on one computer plan to work in the file-mode infobase, the following must be taken into account: the owner of files being created in Linux should be the user in whose account the process to create a file was launched and must be that user’s main group. As a result, the second and all subsequent users (of this computer) will be denied access to files created when attempting to work concurrently in the same file-mode infobase. 1C:Enterprise creates files with the Write and Read permission held by the owner-user and the ownergroup. So in order to enable users to work concurrently, include them in the same group and assign that group to be the owner of the directory where the infobase is located. Next set a sticky-bit per group for this directory by using the chmod g+s ib_dir command, where ib_dir is the name of the directory in which the infobase is located. As a result, the owner of files that are created in that directory becomes the owner-group of the main infobase directory, rather than the main group of the user creating those files.
The procedure for configuring the operating system in order to ensure concurrent interaction with the configuration repository is the same, except that the directory with the configuration repository is used instead of the directory with the infobase.
2.5.2.2. Installing Fonts
To ensure that the 1C:Enterprise works properly, fonts from the Microsoft Core Fonts set must be installed in Linux. This can be performed as follows:
Use the package included in the distribution kit (to be checked in every distribution kit).
For detailed information on the installation process in the Linux RPM mode: http://corefonts.sourceforge.net/.
Manual installation is also available. To do so:
○ Download all files with fonts from the page: http://sourceforge.net/projects/ corefonts/files/the%20fonts/final/.
○ Unpack the files.
○ Save font files in the ~/fonts directory of the user directory (or users directories) from which account the 1C:Enterprise is launched. ~ means the user’s home directory here.
1C:Enterprise searches for TrueType fonts in the following directories:
/usr/share/fonts/truetype/msttcorefonts, which is a standard directory to place fonts for DEB modes of the system.
/usr/share/fonts/truetype/msttcorefonts, which is a standard directory to place fonts to be installed in RPM modes of the system using the corefonts package.
~/.fonts, which is a standard directory to include custom fonts in Linux.
2.5.2.3. OS authentication when Using Apache Web Server
It is possible to configure support of OS authentication for the thin and the web clients when Apache web server is used. In this section, we assume that Apache web server is already installed and configured for access via a web client.
IMPORTANT!
In order to setup OS authentication, the network should have PDC deployed under Windows 2000 or later.
To carry out setup:
Install mod_auth_kerb authentication module. This module is included in the majority of distribution kits, you only need to install the corresponding package. This package is named mod_auth_kerb for Fedora operating system and libapache2-mod-auth-kerb for Debian. If the module is not included in the distribution kit of the operating system used, you can download its source code from the project home page at: http://modauthkerb.sourceforge.net/.
The following installation options are available:
○ The module is installed from the operating system distribution kit. In this case you will only need to restart the web server and the module will be connected;
○ If you compile and install the module yourself (you will find the installation tips at: http://modauthkerb.sourceforge.net/install.html), you will need to add a string shown below to the Apache web server configuration file httpd.conf and restart Apache.
LoadModule auth_kerb_module /path/to/file/mod_auth_kerb.so
For authentication the module requires the Kerberos privacy key issued for HTTP/Server.domain@DOMAIN. This key should be generated following the instructions in the Kerberos authentication setup (see page 46). Note that Account is trusted for delegation should be checked for the account that will be associated with the name HTTP/Server.domain@DOMAIN.
Let us assume that the key file is named HTTP.keytab and is located at the home directory of the user named usr1cv8.
Next, add the following strings to the section describing the virtual directory of the web server:
<Directory "/home/usr1cv8/www/MyApp"> AllowOverride None Options None Order allow,deny Allow from all SetHandler 1c-application ManagedApplicationDescriptor /home/usr1cv8/www/MyApp/default.vrd AuthName "1C:Enterprise web client" AuthType Kerberos Krb5Keytab /home/usr1cv/HTTP.keytab KrbVerifyKDC off KrbDelegateBasi coff KrbServiceName HTTP/Server.domain@DOMAIN KrbSaveCredentials on KrbMethodK5Passwd off KrbMethod Negotiateon Require valid-user </Directory>
You should specify a correct path to the key file and this file should be readable for the user account Apache is started under.
IMPORTANT!
Please note that Kerberos authentication in a domain that contains both Windows 2000 and Windows 2003 controllers, Linux-based web servers and Windowsbased 1C:Enterprise servers, may fail due to specific features of Kerberos implementation on Windows 2000.
2.6. COMPONENT REGISTRATION
The installer registers several components (the COM connection, etc.). Registration is performed as follows:
COM connection. The installer performs "for computer" registration. "For user" registration may be performed with the following command:
regsvr32 -n -i:user comcntr.dll
Client application (V83.Application COM object). The installer (and client application launch with the RegServer key) performs "for computer" registration. If the user does not have enough privileges to perform this operation, the user is prompted to agree to "for user" registration.
